The difference between Microcontrollers and Microprocessors
Microcontrollers and microprocessors are both essential components in embedded systems and computing devices, but they differ significantly in terms of architecture, functionality, and applications.
📚 1. Definition
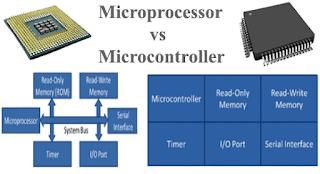
Microcontroller (MCU):
- A compact integrated circuit (IC) that contains a CPU, memory (RAM, ROM/Flash), and peripheral interfaces (GPIO, ADC, timers) on a single chip.
- Designed specifically for embedded applications.
Microprocessor (MPU):
- A CPU (Central Processing Unit) integrated into a single chip, designed to execute instructions and perform calculations.
- External components (RAM, ROM, I/O controllers) are required to build a complete system.
⚙️ 2. Architecture
| Feature | Microcontroller (MCU) | Microprocessor (MPU) |
|---|---|---|
| Components | CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O ports, peripherals integrated | CPU only (requires external peripherals) |
| Memory | On-chip RAM and Flash memory | External RAM, ROM required |
| Bus Width | Typically 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit | 32-bit, 64-bit |
| Clock Speed | Moderate (e.g., 8 MHz to 200 MHz) | High (e.g., 1 GHz to 5 GHz) |
| Power Usage | Low (optimized for efficiency) | High (requires cooling systems) |
| Interrupts | Limited interrupt handling | Advanced interrupt handling |
💼 3. Applications
Microcontroller Applications:
- Embedded systems
- Home appliances (microwaves, washing machines)
- Automotive control systems (ECUs)
- IoT devices (sensors, actuators)
Microprocessor Applications:
- Personal computers and laptops
- Smartphones and tablets
- Servers and data centers
- Gaming consoles
🔋 4. Power Consumption
- Microcontroller: Low power consumption; ideal for battery-operated devices.
- Microprocessor: Higher power consumption; requires dedicated power supply and cooling solutions.
🛠️ 5. Cost
- Microcontroller: Low cost, as peripherals and memory are integrated.
- Microprocessor: Higher cost due to the need for external components.
📝 6. Programming Complexity
- Microcontroller: Easier to program; typically uses C/C++.
- Microprocessor: More complex programming; often involves operating systems (e.g., Linux, Windows) and multithreading.
📊 Key Differences Summary
| Aspect | Microcontroller (MCU) | Microprocessor (MPU) |
|---|---|---|
| Integration | CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O on one chip | CPU only, needs external peripherals |
| Memory | Built-in RAM and ROM | External RAM and ROM |
| Power Consumption | Low | High |
| Processing Power | Moderate | High |
| Clock Speed | Lower (MHz range) | Higher (GHz range) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Applications | Embedded systems, IoT devices | PCs, smartphones, servers |
| Programming | Simpler | More complex, often OS-based |
✅ When to Use Which?
Use a Microcontroller:
- For real-time, low-power, and dedicated tasks.
- When cost and space are constrained.
Use a Microprocessor:
- For high-performance applications requiring multitasking and complex calculations.
- When flexibility and computational power are prioritized.



评论
发表评论